1,3,5-Trioxane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-Trioxane | |||
| Other names
s-Trioxane; 1,3,5-Trioxacyclohexane; Trioxymethylene; Metaformaldehyde; Trioxin
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 102769 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.466 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2230 | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1325 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 90.078 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.17 g/cm3 (65 °C)[1] | ||
| Melting point | 62 °C (144 °F; 335 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K)[1] | ||
| 221 g/L[1] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H228, H335, H361d | |||
| P201, P202, P210, P240, P241, P261, P271, P280, P281, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 45[1] °C (113 °F; 318 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
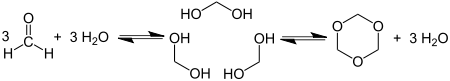
1,3,5-Trioxane, sometimes also called trioxane or trioxin, is a chemical compound with molecular formula C3H6O3. It is a white, highly water-soluble solid with a chloroform-like odor. It is a stable cyclic trimer of formaldehyde, and one of the three trioxane isomers; its molecular backbone consists of a six-membered ring with three carbon atoms alternating with three oxygen atoms.
Production
[edit]Trioxane can be obtained by the acid-catalyzed cyclic trimerization of formaldehyde in concentrated aqueous solution.[2]
Uses
[edit]Trioxane can be used interchangeably with formaldehyde and with paraformaldehyde,[3][4] however the cyclic structure is more stable and it can require high temperatures in order to react. It is a precursor for the production of polyoxymethylene plastics, of which about one million tons per year are produced.[2] Other applications exploit its tendency to release formaldehyde. As such it is used as a binder in textiles, wood products, etc. Trioxane is combined with hexamine and compressed into solid bars to make hexamine fuel tablets, used by the military and outdoorsmen as a cooking fuel.
In the laboratory, trioxane is used as an anhydrous source of formaldehyde.[5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ a b Reuss, Günther; Disteldorf, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Hilt, Albrecht (2000). "Formaldehyde". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_619. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ K. Chen; C. S. Brook; A. B. Smith, III (1998). "6,7-Dihydrocyclopenta-1,3-Dioxin-5(4H)-One". Organic Syntheses. 75: 189. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.075.0189.
- ^ D. S. Connor; G. W. Klein; G. N. Taylor; R. K. Boeckman, Jr; J. B. Medwid (1972). "Benzyl Chloromethyl Ether". Organic Syntheses. 52: 16. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.052.0016.
- ^ W. O. Teeters; M. A. Gradsten (1950). "Hexahydro-1,3,5-Tripropionyl-s-Triazine". Organic Syntheses. 30: 51. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0051.